이지우
2024년 1월 9일
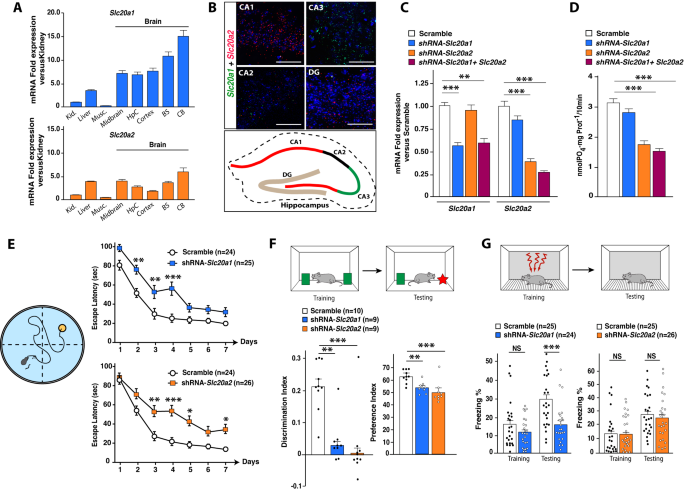
- 뇌 석회화가 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체 SLC20a2의 돌연변이와 관련이 있는 것으로 나타남. Slc20a1과 Slc20a2가 뇌에서 가장 높게 발현되는 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체이고 해마 의존적 학습과 기억의 제어에 관여한다는 것을 보여줌. 또한, 저자들은 Slc20a1과 Slc20a2가 해마에서 차별적으로 분포되어 있으며, 독립적인 유전자 클러스터와 관련되어 있어 서로 다른 메커니즘으로 인지에 영향을 미친다는 것을 밝힘. 따라서 분자, 전기 생리학 및 행동 분석을 조합하여 Slc20a2가 해마 신경 분지와 생존을 선호하는 반면 Slc20a1은 시냅스 가소성을 촉진한다는 것을 보여줌.
Abstract: In recent years, primary familial brain calcification (PFBC), a rare neurological disease characterized by a wide spectrum of cognitive disorders, has been associated to mutations in the sodium (Na)-Phosphate (Pi) co-transporter SLC20A2. However, the functional roles of the Na-Pi co-transporters in the brain remain still largely elusive. Here we show that Slc20a1 (PiT-1) and Slc20a2 (PiT-2) are the most abundant Na-Pi co-transporters expressed in the brain and are involved in the control of hippocampal-dependent learning and memory. We reveal that Slc20a1 and Slc20a2 are differentially distributed in the hippocampus and associated with independent gene clusters, suggesting that they influence cognition by different mechanisms. Accordingly, using a combination of molecular, electrophysiological and behavioral analyses, we show that while Slc20a2 favors hippocampal neuronal branching and survival, Slc20a1 promotes synaptic plasticity. The latter relies on a likely Otoferlin-dependent regulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking, which impacts the GABAergic system. These results provide the first demonstration that Na-Pi co-transporters play key albeit distinct roles in the hippocampus pertaining to the control of neuronal plasticity and cognition. These findings could provide the foundation for the development of novel effective therapies for PFBC and cognitive disorders.
Method: Researchers examined the impact of downregulating Slc20a1 and Slc20a2 gene expression on cognitive functions in C57BL/6 J wild-type male mice. To achieve this, adeno-associated viruses carrying shRNA sequences were injected into the hippocampus to selectively suppress either Slc20a1 or Slc20a2. Post-treatment, a series of behavioral analyses assessed changes in learning and memory abilities. Tasks included the Novel Object Recognition test, which evaluates recognition memory, the Contextual Fear Conditioning test to assess associative memory, and the Morris Water Maze test to examine spatial learning. Additionally, other tests for anxiety-like behaviors, such as the open field test, were conducted to investigate emotional responses linked to Slc20a1 and Slc20a2 downregulation. Further molecular analyses, including transcriptomics and histological evaluations, were employed to understand the underlying mechanisms impacting synaptic plasticity, dendritic morphology, and gene expression patterns.
Conclusion: Results revealed that downregulation of Slc20a1 and Slc20a2 genes in the hippocampus produced distinct effects on cognition and neuronal health. Slc20a1 downregulation impaired synaptic plasticity by reducing dendritic spine density and altering neurotransmitter release, with increased expression of genes related to the GABAergic system. Behavioral tests showed that Slc20a1 deficiency disrupted contextual fear memory but not anxiety-like behaviors. In contrast, Slc20a2 downregulation primarily affected neuronal survival, reducing the number of mature neurons and increasing neuroinflammation. Mice with reduced Slc20a2 expression demonstrated deficits in spatial and episodic memory, alongside heightened anxiety-like behavior. These behavioral effects were accompanied by a significant upregulation of genes linked to inflammation and immune responses in the hippocampus. Interestingly, neither Slc20a1 nor Slc20a2 alterations significantly impacted phosphate transport, indicating that their roles in cognition and neuronal plasticity are largely independent of their function as sodium-phosphate cotransporters. The findings suggest that Slc20a1 and Slc20a2 independently regulate memory, learning, and emotional behaviors through distinct molecular pathways
(한글 요약)
-소개: 최근 논문에 따르면 뇌 석회화가 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체 SLC20a2의 돌연변이와 관련이 있는 것으로 나타남. 그러나 뇌에서 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체의 기능적 역할에 대해 밝혀진 바가 많지 않음. 저자들은 Slc20a1과 Slc20a2가 뇌에서 가장 높게 발현되는 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체이고 해마 의존적 학습과 기억의 제어에 관여한다는 것을 보여줌. 또한, 저자들은 Slc20a1과 Slc20a2가 해마에서 차별적으로 분포되어 있으며, 독립적인 유전자 클러스터와 관련되어 있어 서로 다른 메커니즘으로 인지에 영향을 미친다는 것을 밝힘. 따라서 분자, 전기 생리학 및 행동 분석을 조합하여 Slc20a2가 해마 신경 분지와 생존을 선호하는 반면 Slc20a1은 시냅스 가소성을 촉진한다는 것을 보여줌. 또한, 시냅스 소포 수송의 오토페를린 의존적 조절에 의존하며, 이는 GABAergic 시스템에 영향을 미침. 이러한 결과는 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체가 신경 가소성과 인지의 제어와 관련하여 뇌 석회화 및 인지 장애에 대한 새로운 효과적인 치료법 개발의 기초를 제공할 수 있음
-실험 방법: 이 연구에서 연구자들은 C57BL/6J 야생형 수컷 마우스에서 Slc20a1 및 Slc20a2 유전자 하향 조절에 따른 인지 기능에 대한 영향을 조사함. 이를 확인하기 위해 shRNA를 사용하여 Slc20a1 또는 Slc20a2를 선택적으로 억제함. 이후, 행동 분석 테스트를 통해 학습 및 기억 능력의 변화를 평가함. 이를 평가하기 위해, 인식 및 기억을 평가할 수 있는 새로운 사물 인식 테스트, 연관 기억을 평가하는 상황적 공포 조절 테스트, 그리고 공간 학습을 검사할 수 있는 모리스 워터 미로 테스트가 진행됨. 또한 개방형 필드 테스트와 같은 불안과 유사한 행동에 대한 다른 테스트를 수행하여 Slc20a1 및 Slc20a2 발현 조절에 따른 감정적 반응을 조사함. 인실리코 및 조직학적 평가를 포함하여 추가적으로 분자 분석을 진행하여 시냅스의 가소성, 수상돌기 형태 및 유전자 발현 패턴에 영향을 미치는 근본적인 메커니즘을 확인함.
-결과: 연구 결과에 따르면 해마에서 Slc20a1과 Slc20a2 유전자의 하향 조절은 인지와 신경 건강에 뚜렷한 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타남. Sc20a1 하향 조절은 수상돌기 가시 밀도를 감소시키고 신경전달물질 방출을 변화시켜 시냅스 가소성을 손상시켰으며, GABAergic 시스템과 관련된 유전자의 발현이 증가함. 행동 검사 결과 Slc20a1 억제는 공포 기억을 방해했지만 불안과 같은 행동에는 영향을 미치지 않음. 반면 Slc20a2 하향 조절은 주로 신경 생존에 영향을 미쳐 성숙한 신경 세포의 수를 줄이고 신경 염증을 증가시킴. Slc20a2 발현이 감소한 마우스는 공간 기억과 에피소드 기억에 결함이 있었고, 불안과 같은 행동이 증가함. 이러한 행동적 효과에는 해마에서 염증과 면역 반응과 관련된 유전자의 상당한 상향 조절이 동반됨. 흥미롭게도, Slc20a1이나 Slc20a2 변화는 인산 수송에 큰 영향을 미치지 않았으며, 이는 인지와 신경 가소성에서의 역할이 나트륨-인산 공동 수송체로서의 기능과 크게 독립적임을 시사함. 따라서, 이 연구 결과는 Slc20a1과 Slc20a2가 서로 다른 분자 경로를 통해 기억, 학습 및 감정적 행동을 독립적으로 조절한다는 것을 알 수 있음.